Suicide prevention for older adults has become a critical public health issue as this demographic faces the highest rates of suicide while often lacking adequate mental health resources. Recent studies have shown alarming trends, particularly among adults aged 75 and older, highlighting the urgent need for targeted interventions to support their unique emotional and mental health challenges. Despite the recognition of this crisis, online suicide prevention initiatives frequently overlook the specific needs of older adults, leading to an imbalance in resource allocation. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) report a rising suicide rate in this age group, underscoring the importance of tailored programs that address social isolation and mental health concerns. By facilitating access to appropriate support systems and resources, we can create a more responsive approach to elder suicide prevention, ensuring that older adults are not left behind in the fight against this tragic outcome.
Addressing the issue of suicide among senior citizens requires a compassionate approach that understands their unique circumstances and challenges. Elderly individuals, particularly those over the age of 75, experience heightened risks of self-harm and require specialized mental health resources to mitigate factors contributing to this crisis. With social isolation and loneliness often exacerbating feelings of despair, it is crucial to develop comprehensive strategies aimed at these vulnerable populations. Enhancing online suicide prevention efforts tailored for geriatric mental health can bridge the gap in support for older adults, utilizing digital platforms that they increasingly turn to for help. By investing in innovative outreach and intervention strategies, we can create a safer environment for our seniors, ultimately reducing the incidence of suicide in this demographic.
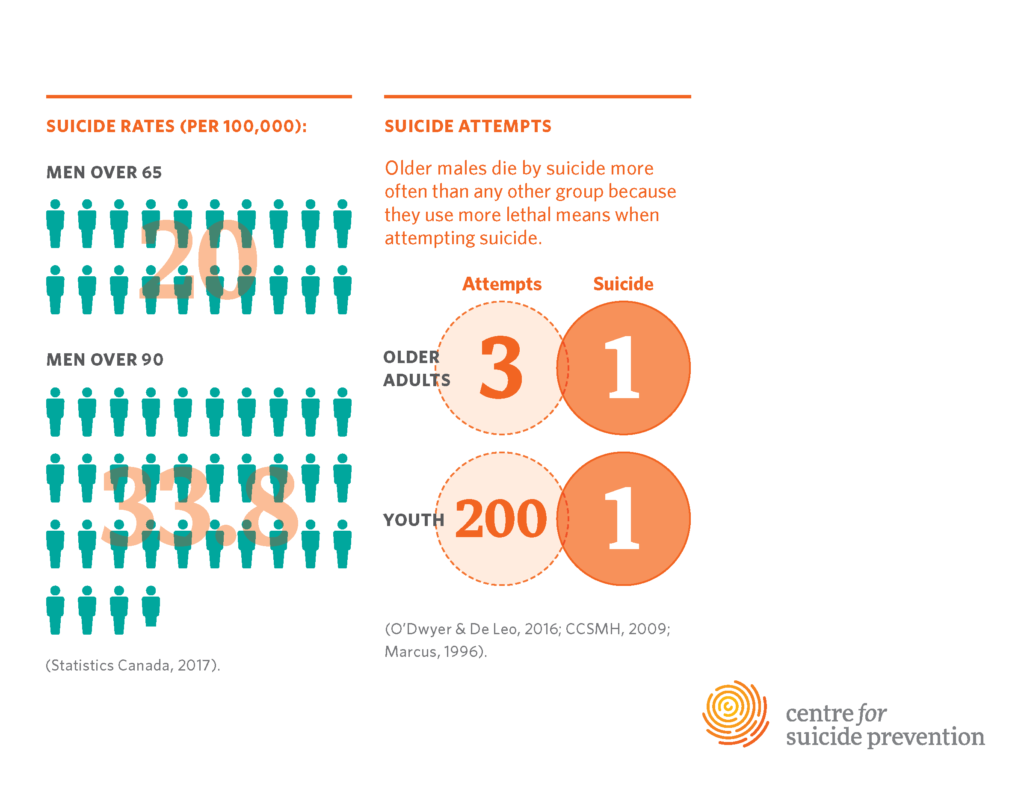
Understanding the High Suicide Rates Among Older Adults
Recent data reveals that older adults, especially those aged 75 and above, experience the highest suicide rates in comparison to other age groups. The statistics provided by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) indicate a troubling rate of approximately 20.3 per 100,000 among this demographic. This phenomenon may be attributed to various factors, including social isolation and inadequate mental health support tailored to older individuals. The increasing trend of elder suicide points to fundamental gaps in our societal structures that fail to provide necessary emotional and psychological aid for our senior citizens.
Despite growing awareness of older adults’ mental health challenges, many national suicide prevention organizations seem to overlook this vulnerable group. Research from Harvard-affiliated McLean Hospital highlights a significant imbalance in the online resources available for suicide prevention targeted at older adults. While these organizations promote campaigns aimed at younger demographics, older individuals, who are at a critical juncture needing support, are often left with limited resources. This disparity underscores the urgent requirement to prioritize mental health resources specifically designed to address the unique needs of older adults.
The Impact of Social Isolation on Elderly Mental Health
Social isolation plays a critical role in the mental health of older adults, significantly contributing to feelings of loneliness and despair. Many seniors live alone or are disconnected from community support systems, which can exacerbate underlying mental health issues. This isolation is especially detrimental as it limits their access to social interaction and the emotional support that is vital for maintaining well-being. Institutions that provide support for older adults must recognize and address these barriers by fostering community engagement and ensuring they have safe and accessible platforms for social connection.
Addressing social isolation includes promoting mental well-being through activities and programs designed specifically for older adults. Engaging these individuals through group activities, mental health workshops, and peer-support forums can not only enhance their quality of life but also serve as a preventive measure against issues like depression and suicidal ideation. By bridging the gap between older adults and community resources, we can mitigate aspects of isolation and promote a sense of belonging, essential for improving geriatric mental health.
The Role of Online Resources in Suicide Prevention for Older Adults
As more seniors turn to the internet for health-related information, the role of online suicide prevention resources becomes paramount. Many older adults seek help through online platforms, and the expectation is that reputable organizations will provide accessible mental health resources that directly cater to their needs. However, a troubling conclusion drawn from the research is that these resources are not only scarce but also poorly advertised, making it difficult for seniors to find help at a time when they need it most. This gap in resource availability could hinder timely interventions, exacerbating the seriousness of their situation.
To effectively combat the rising suicide rates in older adults, it is essential that suicide prevention initiatives leverage online platforms strategically. Tailored content that resonates with older adults, utilizing language and visuals appropriate for this age group, can enhance engagement and resource accessibility. Efforts should focus on creating user-friendly websites and platforms where elderly individuals can easily navigate resources related to mental health, thereby ensuring they are more likely to seek help when needed.
Addressing the Need for Targeted Campaigns in Suicide Prevention
There is an urgent need for public-facing suicide prevention campaigns to specifically target the elderly population. Current strategies primarily focus on younger age groups, leaving older adults without adequate resources to address their significant risk of suicidal thoughts. As noted by Ipsit Vahia, there is a pressing demand for adaptation in how resources are presented to better serve this demographic. Campaigns must engage older adults effectively, addressing their unique challenges while promoting accessible mental health support.
In crafting effective campaigns, it is crucial to involve older adults in the design process—to better understand their perceptions, experiences, and preferences. This involvement can help tailor messages that resonate, ultimately encouraging older individuals to seek help. Funding for these initiatives must increase to ensure that efforts are sustained and impactful, leading to strategic outreach that elevates the mental health standards for the elderly population worldwide.
The Importance of Geriatric Mental Health Research
Research directed toward geriatric mental health is a vital component of improving the well-being of older adults. As life expectancy increases, so does the necessity of understanding the mental health challenges faced by the elderly. Ongoing studies, like those conducted by the National Institute on Aging, are essential in revealing the complexities surrounding late-life suicide, enabling researchers and clinicians to identify at-risk individuals promptly. Supporting such studies not only enhances the knowledge base around elderly mental health but also contributes to the development of effective prevention strategies.
In parallel, increasing public awareness about the importance of mental health research related to older adults helps destigmatize seeking help. By encouraging broader investment in geriatric mental health studies, we can create a more informed society about the pressing needs of older individuals. Funding such initiatives ensures that we equip healthcare providers with the tools necessary to address the psychological issues that contribute to suicidal behavior in seniors.
Creating Support Systems for Older Adults
Establishing comprehensive support systems for older adults is a pivotal part of suicide prevention strategies. These systems should include accessible mental health resources, community outreach programs, and platforms for social engagement. Creating an environment that promotes the physical and mental health of older adults can significantly reduce feelings of loneliness and isolation, paving the way for healthier relationships and social connections. Crucially, combining these efforts with community education on recognizing warning signs of mental distress can empower individuals to reach out and offer help.
Support systems must also involve family members and caregivers in the process, equipping them with the knowledge and resources needed to provide proper support. This collective approach ensures that older adults feel valued and connected, which significantly mitigates risks associated with suicidal thoughts. As mental health resources and awareness expand in these communities, we can work towards building a more robust safety net for our elderly population.
Using Technology to Enhance Older Adults Support
The integration of technology into support systems for older adults holds great promise for enhancing mental health resources. Digital platforms can facilitate communication and provide instant access to support services, making it easier for seniors to seek help without facing the stigma often associated with mental health issues. Online counseling and telehealth options can offer vital support, allowing older adults to communicate with mental health professionals from the comfort of their homes, therefore, improving geriatric mental health outcomes.
Moreover, technology can foster community connections through social media and dedicated online forums where older adults can interact and share experiences. These connections can alleviate feelings of isolation and encourage participation in available mental health programs. By utilizing technology as a tool for connection and support, we stand to make significant advancements in the well-being of older adults, steering the collective efforts toward reduced suicide rates in this demographic.
Importance of Funding for Elderly Mental Health Initiatives
Sustained funding for elderly mental health initiatives is essential to address the growing issue of suicide amongst older adults. Despite the increasing recognition of mental health needs, financial resources for geriatric mental health programs are often limited. To effectively counter the rising rates of suicide in this demographic, consistent investment into research, community programs, and online resources is necessary. Funds should be channeled into developing comprehensive campaigns targeting older adults and ensuring resources are readily available and accessible.
Moreover, promoting partnerships between government agencies and nonprofit organizations can enhance the capacity to deliver effective mental health services. By strategically directing funding toward innovative solutions, we can establish supportive environments that prioritize the mental health of older adults, ultimately leading to healthier and more connected communities.
Encouraging Conversations About Suicide Prevention
Facilitating open conversations about suicide prevention among older adults is critical in dismantling the stigma surrounding mental health issues. Many seniors may feel embarrassed or reluctant to discuss their feelings, which contributes to the alarming rates of suicidal ideation. Creating safe spaces where elderly individuals can share their experiences and seek support can foster relief and awareness. These discussions can be encouraged through community workshops and education programs focusing on emotional well-being and coping strategies.
Encouragement for family members and caregivers to engage in dialogue with older adults about mental health can significantly impact their willingness to seek help. By normalizing conversations about vulnerability, fear, and despair, we can create a culture that values emotional expression. This proactive approach will not only empower seniors to share their struggles but may also prevent crises before they escalate, saving lives in the process.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the statistics related to elderly suicide rates?
Elderly suicide statistics reveal that individuals aged 75 and older have the highest rates of suicide among all age groups, with rates as high as 20.3 per 100,000 according to the CDC. This alarming trend highlights the urgent need for targeted suicide prevention efforts for older adults.
What mental health resources are available for older adults at risk of suicide?
While there is a critical need for mental health resources specifically for older adults, many existing resources are not easily accessible. Communities can benefit from comprehensive programs that address the unique mental health needs of older adults, including online suicide prevention resources tailored to their circumstances.
How can online suicide prevention initiatives better support older adults?
Online suicide prevention initiatives need to be designed with older adults in mind, offering easy-to-navigate resources that address their specific risks and challenges. Increased visibility and accessibility of these resources can significantly aid in preventing suicide among older adults.
What role does social isolation play in older adults’ risk of suicide?
Social isolation and loneliness are critical factors contributing to the rising suicide rates among older adults. As these individuals may have diminished social support systems, targeted interventions should focus on enhancing social connections and mental health support for this demographic.
Why is geriatric mental health important in suicide prevention?
Geriatric mental health is vital for suicide prevention as it encompasses the specific mental health challenges faced by older adults. Tailored mental health resources can help address the unique needs, ensuring that older adults receive the appropriate support to reduce their risk of suicide.
What can families do to support older adults who may be suicidal?
Families can play a crucial role in suicide prevention by fostering open communication, providing emotional support, and encouraging older adults to seek professional help. Awareness of available mental health resources can empower families to assist their loved ones effectively.
How can increased funding improve suicide prevention for older adults?
Increased funding for suicide prevention programs specifically targeting older adults can facilitate research and the development of tailored resources. This funding can help organizations create effective online initiatives and community-based programs to address elder suicide risks effectively.
What steps can individuals take to seek help for an older adult at risk of suicide?
Individuals concerned about an older adult at risk of suicide should encourage them to reach out to mental health professionals, utilize helplines, or engage with community support services. Increasing awareness of available mental health resources is essential for effective intervention.
| Key Points |
|---|
| Older adults aged 75+ have the highest suicide rates but lack resources. |
| National organizations do not provide easily accessible resources for older adults. |
| The study indicates an imbalance in targeted online suicide prevention efforts. |
| Increased use of internet resources by older adults is noted for seeking health information. |
| There’s a growing need for tailored prevention programs for older adults, considering their unique healthcare needs. |
| Social isolation, loneliness, and biases contribute to increased suicide risk among older adults. |
| Public campaigns specific to older adults are urgently needed due to high suicide rates. |
| Increased funding and research is essential for effective late-life suicide prevention efforts. |
Summary
Suicide prevention for older adults is a critical issue, as they face the highest rates of suicide yet have the least amount of accessible resources. The recent study emphasizes the urgent need to improve online suicide prevention efforts that cater specifically to this demographic. Addressing the unique healthcare needs of older adults through tailored programs and public campaigns can help reduce the rising suicide rates in this population. It is essential to enhance accessibility to resources and foster social connections to combat loneliness and isolation—a significant factor contributing to the suicide crisis among older adults.