Is sugar addictive? This intriguing question has sparked considerable debate among nutrition experts and healthcare professionals alike. While sugar does not meet the strict clinical criteria for addiction like substances such as alcohol and nicotine, it undeniably influences our cravings and eating behaviors. The effects of sugar extend beyond mere taste preferences; they can trigger physiological and psychological responses that are hard to ignore. Understanding the nuances of sugar addiction, including its health effects, can guide us in cutting sugar intake and managing those relentless sugar cravings.
The topic of sugar dependency raises important issues regarding our everyday diets. Commonly referred to as sugar cravings, this phenomenon involves an overwhelming desire for sweet foods that many experience regularly. As we navigate our nutrition, it’s vital to recognize the impact of added sugars found in ultra-processed foods that often lead to habitual consumption. When exploring the health effects of sugar, recognizing the challenges of reducing sugar intake gradually becomes essential for maintaining a balanced diet. Consequently, understanding this relationship between our cravings and sugar can equip us with better strategies for healthier choices.
Understanding Sugar Addiction
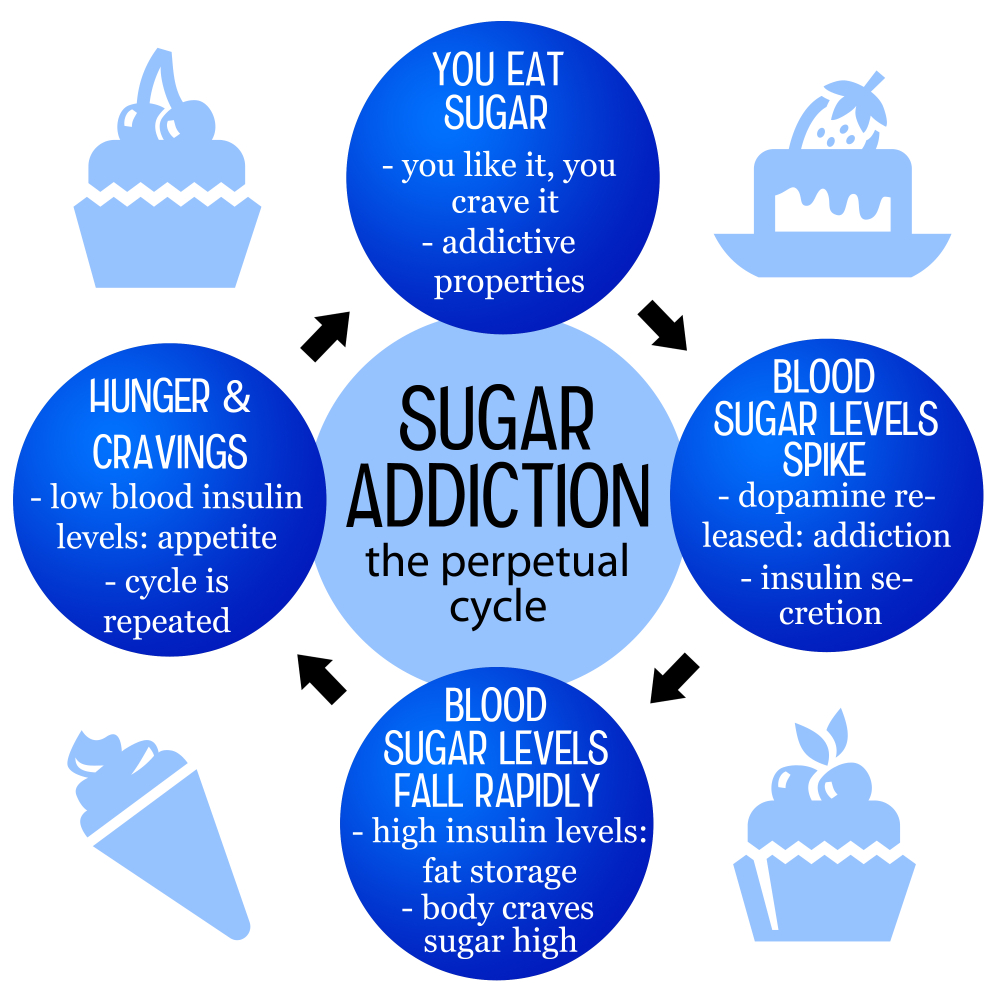
When discussing sugar addiction, it’s important to recognize that while sugar does not meet the clinical criteria typically associated with addictive substances such as alcohol or nicotine, it can still prompt cravings and compulsive behaviors. Research shows that high sugar consumption leads to neurochemical responses similar to those seen with more widely accepted addictive substances. While we must be cautious in labeling it as an addiction, the effects of sugar on the brain and body can’t be ignored. Individuals often find themselves reaching for sugary snacks and beverages, creating a cycle that can be tough to break.
Moreover, the prevalence of ultra-processed foods, laden with added sugars, exacerbates the issue. These foods are engineered to be hyper-palatable, making them difficult to resist. As we consume these sweet products, our bodies become accustomed to high levels of sugar, resulting in heightened cravings when we try to cut back. This experience can mimic withdrawal symptoms, including headaches and mood swings, further complicating one’s relationship with sugar. Understanding these factors can help people approach their sugar intake more mindfully.
The Effects of Sugar on Health
The health effects of sugar are a topic of ongoing research and debate. Excessive sugar consumption is linked to a host of health issues, ranging from obesity and type 2 diabetes to heart disease. The average American ingests around 20 teaspoons of added sugar each day, significantly above the recommended limits set by health organizations. These surpluses not only contribute to weight gain but also impact metabolic health, leading to increased cravings and a reliance on sugar as a quick source of energy.
Furthermore, regularly consuming high-sugar foods and drinks can cause long-term damage to our nutritional balance. When substantial amounts of sugar are ingested, it can lead to altered gut microbiota, insulin resistance, and even inflammation. By being aware of the effects of sugar and adjusting our intake accordingly, we can improve our overall health and reduce our risk of chronic illnesses.
Cutting Sugar Intake: Strategies for Success
Cutting sugar intake can seem daunting, but it is achievable with the right strategies in place. First, it’s crucial to read labels on foods to better understand the sugar content of the products we consume. Knowledge is power, and by knowing how much sugar is in our foods, we can make informed choices. Gradually reducing sugar intake rather than eliminating it entirely helps to minimize withdrawal symptoms and makes the process more manageable.
Incorporating more whole foods into our diet is another effective way to naturally lower sugar consumption. Foods such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins not only provide essential nutrients but also help satisfy cravings for sweets in a healthier manner. By finding alternative ways to indulge in sweetness, such as using natural sweeteners like honey or fruit-based options, we can still enjoy flavorful meals without the adverse effects of excessive added sugar.
Dealing with Sugar Cravings
Sugar cravings often arise due to a variety of factors, including emotional triggers and habitual consumption patterns. Understanding the origins of these cravings is vital for effectively managing them. Stress, boredom, or even fatigue can lead us to seek out sugary comfort foods. Being aware of these triggers allows us to develop healthier coping mechanisms, such as engaging in physical activity or practicing mindfulness instead of reaching for that sugary snack.
It can also be helpful to keep healthier snack options readily available. Stocking up on fruits, nuts, or yogurt can provide satisfying alternatives when sugar cravings strike. Additionally, staying hydrated and ensuring balanced meals can prevent the spikes and drops in blood sugar levels that often lead to cravings. By taking proactive steps, we can reduce the frequency and intensity of sugar cravings, leading to healthier eating habits.
Is Sugar Addictive? Exploring the Myths
The question ‘Is sugar addictive?’ sparks much debate, and while sugar does not align with traditional definitions of addiction, it can produce significant psychological and physiological effects. The increase in cravings associated with sugar intake resembles addiction patterns observed in substance abuse, complicating how we view this common dietary component. Yet, labeling sugar as an addictive substance might detract from its role as a necessary macronutrient needed for energy.
Moreover, understanding the nuanced relationship between sugar and addiction can aid individuals in approaching their diets with a balanced mindset. Rather than viewing sugar as an outright enemy, we can appreciate that moderate sugar consumption is a part of a healthy diet when managed responsibly. This perspective could lead to more sustainable eating habits, promoting a better relationship with food overall.
The Dosage Dilemma: Finding Balance with Sugar
While the conversation around sugar often focuses on its negative effects, it’s crucial to consider the importance of dosage. Not all sugars are inherently bad; natural sugars found in fruits and whole foods are vital for providing energy and essential nutrients. The challenge lies in discerning between these healthy sources of sugar and added sugars in processed foods that can lead to health issues if consumed in excess.
Being mindful of portion sizes and aiming for moderation in our sugar intake can transform our diets for the better. The American Heart Association’s recommendations guide individual sugar consumption based on gender and age, further emphasizing the importance of balance rather than complete elimination. By implementing moderation, we can enjoy the benefits of sugar without succumbing to its potential health risks.
Mindful Eating: The Key to Reducing Sugar Consumption
Mindful eating practices can play a pivotal role in reducing sugar intake. This approach encourages individuals to pay attention to their eating habits and to savor food, making them more aware of their cravings and consumption patterns. By being fully present during meals, individuals can better recognize their body’s signals and differentiate between hunger and emotional cravings.
Practicing mindful eating can also reduce mindless snacking on sugary foods. Keeping a food journal or maintaining a gratitude log can further help individuals track their eating habits and foster a healthier relationship with food. Ultimately, mindful eating is about achieving a more conscious approach to nutrition, empowering individuals to make better food choices aligned with their health goals.
The Importance of Education on Sugar and Health
Education plays a crucial role in combating the adverse health effects of sugar. Increasing public awareness about added sugars and their implications is essential in guiding people toward healthier dietary choices. Nutrition education initiatives in schools, communities, and healthcare settings can provide individuals with knowledge about how to read food labels, the significance of moderating sugar intake, and identifying healthier alternatives.
Such educational programs can empower people to take control of their health and make informed decisions when it comes to sugar consumption. By fostering a better understanding of the impact of sugar on our bodies, individuals can engage in proactive strategies, ultimately leading to healthier behaviors and outcomes. This awareness sets the stage for reducing the overall intake of added sugars in communities.
Long-Term Strategies for Reducing Sugar Intake
Implementing long-term strategies for reducing sugar intake is fundamental to maintaining health and well-being. One effective method is to set achievable goals and gradually replace high-sugar items with healthier options. Instead of aiming for perfection, allowing for occasional treats can prevent feelings of deprivation and promote a more sustainable approach to dietary changes.
Additionally, planning meals and snacks in advance can help keep individuals on track. Preparing wholesome snacks and having them readily available can diminish the temptation to reach for sugary alternatives. By focusing on long-term habits rather than quick fixes, individuals can achieve lasting changes that improve their overall health and relationship with sugar.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is sugar addictive like alcohol or nicotine?
No, sugar is not classified as an addictive substance in the same way alcohol and nicotine are. While sugar can lead to cravings and compulsive eating behaviors, and has some addictive qualities, it doesn’t meet the strict clinical criteria for addiction. It’s important to manage sugar intake for health, but moderate consumption can be part of a balanced diet.
What are the effects of sugar on cravings and eating behavior?
The effects of sugar on cravings can result in compulsive eating, especially when consumed in large amounts found in ultra-processed foods. These foods not only contain added sugars but also unhealthy fats, making them more appealing and heightening cravings. Reducing sugar intake gradually can help mitigate withdrawal-like symptoms such as headaches and anxiety.
How can I manage my sugar cravings effectively?
To effectively manage sugar cravings, it’s crucial to gradually reduce added sugar intake rather than cutting it out completely. Start by checking food labels and being mindful of hidden sugars in your diet, especially from sugary snacks and beverages. Incorporating whole foods like fruits and vegetables can also help satisfy your sweet tooth in a healthier way.
What are the health effects of excess sugar consumption?
Consuming excess sugar can lead to various health issues, including obesity, type 2 diabetes, and heart disease. The American Heart Association recommends limiting added sugar intake to 9 teaspoons for men, 6 for women, and even less for children to minimize health risks. Being aware of your sugar consumption is vital for maintaining overall health.
What happens when you cut sugar intake suddenly?
Cutting sugar intake suddenly can lead to withdrawal-like symptoms, including headaches, dizziness, and anxiety. This is due to the body’s reaction to the absence of sweet foods, which can trigger cravings. It’s generally more effective to gradually decrease sugar intake to avoid these negative effects and establish healthier eating habits.
Why is it so hard to cut sugar from my diet?
It can be challenging to cut sugar from your diet due to its presence in many processed foods and its palatable nature, which creates cravings. These cravings can feel strong and can lead to compulsive eating behaviors. Understanding sugar’s role in your diet and gradually reducing intake can help manage these challenges.
Can I eliminate sugar from my diet completely?
While it’s possible to significantly reduce sugar intake, completely eliminating it can be impractical and unnecessary, as sugar occurs naturally in many healthy foods like fruits and vegetables. Instead, aim for low to moderate consumption of added sugars to balance enjoyment and health.
Is it harmful to consume sugar in moderation?
No, consuming sugar in moderation is not harmful for most people. In fact, small amounts of sugar can enhance flavor and pleasure in foods. The key is to maintain a balanced diet and keep added sugar intake within recommended limits to avoid potential health risks.
| Key Points | Details |
|---|---|
| Cravings | Real cravings exist, but labeling sugar alongside substances like alcohol and nicotine may be misleading. |
| Addictiveness Debate | Though sugar can prompt compulsive behaviors, it doesn’t qualify as an addictive substance under clinical definitions. |
| Ultra-Processed Foods | Many foods high in refined sugar lead to heightened cravings and habitual consumption due to their taste and availability. |
| Withdrawal Symptoms | Stopping sugar can induce mild withdrawal symptoms e.g., headaches and anxiety, but they are less intense than for true addictions. |
| Sugar is Necessary | Sugar is found in many necessary foods (e.g., fruits, dairy) making total elimination impractical. |
| Recommended Intake | The average American consumes 20 teaspoons of added sugar daily, which exceeds the American Heart Association’s recommendations. |
| Gradual Reduction | Gradually reducing sugar intake is advised over going ‘cold turkey’ to avoid overwhelming cravings. |
| Balanced Consumption | Moderate sugar consumption can enhance food enjoyment without significant health risks. |
Summary
Is sugar addictive? This intriguing question has sparked much debate among nutrition experts. While sugar can lead to cravings and compulsive eating behaviors, it does not meet the strict clinical criteria for addiction as seen with substances like alcohol or nicotine. Instead, it is important to view sugar in moderation as part of a balanced diet, recognizing that while it may contribute to cravings, its essential presence in various foods makes it differ fundamentally from addictive substances. Thus, rather than viewing sugar as purely addictive, it should be understood within the context of consumption habits and dietary balance.